Generate An Sftp Private Key
- Generate Sftp Ssh Key
- Generate An Sftp Private Key Tool
- Generate An Sftp Private Key Password
- Sftp Private Key Authentication
- Sftp With Key
The.pub file is your public key, and the other file is the corresponding private key. If you don’t have these files (or you don’t even have a.ssh directory), you can create them by running a program called ssh-keygen, which is provided with the SSH package on Linux/macOS systems. Jun 22, 2012 About SSH Keys. Secure Shell (better known as SSH) is a cryptographic network protocol which allows users to securely perform a number of network services over an unsecured network. SSH keys provide a more secure way of logging into a server with SSH than using a password alone. While a password can eventually be cracked with a brute force attack. 2 Ways to Generate an SFTP Private Key with JSCAPE MFT Server 1. Obtaining an SFTP private key via the Key Manager. Obtaining an SFTP private key via the User Web UI.
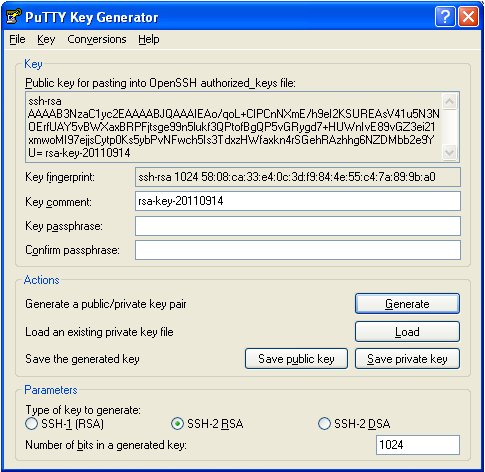
Mar 27, 2019 The private key is able to generate signatures. A signature created using your private key cannot be forged by anybody who does not have that key; but anybody who has your public key can verify that a particular signature is genuine. So you generate a key pair on your own computer, and you copy the public key to the server under a certain name. Generate a Secure Shell (SSH) key pair for an SFTP dropbox - To generate an SSH key pair on a Windows machine: Download PuTTYgen.exe and run it. Select the RSA radio button in the Parameters section near the bottom of the page. Click the Generate button. Move the mouse around in the blank area.
FileZilla is most popular FTP client used by users for connecting FTP server from local system. It has lots of features to use a remote server. But most of them don’t have more idea of how to connect sftp using Filezilla.
If you don’t want to use a password, you can simply use SSH private key with Filezilla to authenticate on a key basis. This article will help you to How to import private key in Filezilla for sftp access.
Download FileZilla Client: click here to download filezilla client
Requirement
FileZilla Client: You must have Filezilla client installed on your system.
SSH Private Key: You must have ssh private key to attach with Filezilla client.
Step 1 – Start Filezilla
I hope you better know how to start Filezilla on your system. We can start Filezilla using a shortcut or through program files or command line.
Step 2 – Add Key in Filezilla
Follow the given below screenshots to add primary key in filezilla.
2.1
Go to
2.2
Select
2.3
Select private key file. You Key file will be added in List. Now Just click
Some times Filezilla prompt to convert key in the case provided key is not in the correct format which Filezilla supports. Feel free to convert the file and save with some other name.
Step 3 – Connect to SFTP Server
Enter the detail of Host, Username and Port ( if not using default ) and click on
.
You may also visit https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=laN-dXhrttA for video tutorial.
Overview
SFTP provides an alternative method for client authentication. It's called SFTP public key authentication. This method allows users to login to your SFTP service without entering a password and is often employed for automated file transfers. In this post, we'll walk you through the process of setting up this kind of authentication on the command line. It's really easier to do this on a GUI-based interface but if you simply love doing things on the terminal, this post is for you.
Note: SFTP (through SSH) is usually installed on Linux distros, so we'll be using Linux for both the (SFTP) server and client machines in this tutorial.
1. Create the .ssh directory
The first thing you'll want to do is create a .ssh directory on your client machine. This directory should be created inside your user account's home directory. Login to your client machine and go to your home directory. Just enter:
cd ~
You should now be inside your home directory.
In the screenshot below, we used ls -a to list all the files and folders in our home directory.

To add the .ssh directory, just enter:
Generate Sftp Ssh Key
mkdir .ssh
So now, when we list all the files in our home directory, we can already see the .ssh directory. /openssl-generate-key-pair-c.html.
You'll want to make sure only the owner of this account can access this directory. To do that, change the user permissions of the directory by running:
chmod 700 .ssh
2. Run ssh-keygen
Next, we need to populate our .ssh directory with the public/private key pair we'll be using for our sftp key authentication. Run the ssh-keygen command:
ssh-keygen
Not familiar with SFTP keys? Click that link to learn more about them.
Immediately after running the ssh-keygen command, you'll be asked to enter a couple of values, including:
Generate An Sftp Private Key Tool
- The file in which to save the private key (normally id_rsa). Just press Enter to accept the default value.
- The passphrase - this is a phrase that functions just like a password (except that it's supposed to be much longer) and is used to protect your private key file. You'll need it later, so make sure it's a phrase you can easily recall.
As soon as you've entered the passphrase twice, ssh-keygen will generate your private (id_rsa) and public (id_rsa.pub) key files and place them into your .ssh directory. You'll also be shown the key fingerprint that represents this particular key.
To verify whether the files were really created successfully and placed in your .ssh directory, go to your .ssh directory and list the files as shown:
Here's a sample of how the contents of an SFTP private key file (id_rsa) looks like, viewed using the less command.
and here's how the contents of a SFTP public key file (id_rsa.pub) looks like:
Again, we'd like to make sure only the owner can read, write, and execute these files. So run the chmod command yet again to assign the appropriate permisssions:
chmod 700 ./id_rsa.*
Now that we have a .ssh directory in our client machine (populated with the private/public key pair), we now have to create a corresponding .ssh directory on the server side.
3. Create .ssh directory on SFTP server
Login to your SFTP server via SSH. We're assuming you already have a user account on your SFTP server and that the service is already up and running. Don't worry too much if you encounter a notification saying 'The authenticity of host .. can't be established .. Are you sure you want to continue connecting?' Barring any untoward incidents, it's just SSH informing you that a trust relationship between your server and your client has not yet been established. Just type in 'yes', hit [enter], and enter your password.
Recommended article: Setting Up an SFTP Server
Once you're logged in, navigate to your user account's home directory (on the server) and (just like in your client machine), create a .ssh directory.
Assign the required permissions for this directory by running:
chmod 700 .ssh
Next, navigate to your newly created .ssh directory and create the file authorized_keys. This file will be used to hold the contents of your public key. Here, we create this file by using the touch command like so:
touch authorized_keys
Yes, you need to run chmod on this file too:
chmod 700 authorized_keys
When you're done, exit your SSH session.
4. Run ssh-copy-id
Now it's time to copy the contents of your SFTP public key to the authorized_keys file. The easiest way to do this would be to run the ssh-copy-id command. The ssh-copy-id program is usually included when you install ssh. The syntax is:
ssh-copy-id -i id_rsa.pub user@remoteserver
where user is just the username used earlier and remoteserver is just the IP address/hostname of your SFTP/SSH server.
You'll then be asked to enter your account's password. This is just the same password you used to login via SSH earlier.
5. Login SFTP SSH key based authentication
To verify that everything went well, ssh again to your SFTP server. This time, you'll be asked to enter the passphrase instead of the password.
Navigate to your .ssh directory and view the contents of the authorized_keys file. It should contain exactly the same characters found in your SFTP public key file.
Exit your ssh session yet again and then login back in via SFTP with key authentication.
Generate An Sftp Private Key Password
Note: Had you not assigned any passphrase when you created your public and private keys using ssh-keygen, you would have been able to login just like this:
That's it. Now you know how to setup SFTP with public key authentication using the command line. There's actually an easier way to do this. The article 2 Ways to Generate an SFTP Private Key will show you a couple of GUI-based methods that arrive at the same result.
Get started
Looking for an SFTP server? Download the free, fully-functional evaluation edition of JSCAPE MFT Server now.
Sftp Private Key Authentication
Sftp With Key
Be up-to-date on tips like this. Follow us on Twitter!